An INNER JOIN returns only the rows where there is a match in both tables based on the join condition. If a row in either table does not have a corresponding match, it will be excluded from the result.
SELECT * FROM TableA
INNER JOIN TableB
ON TableA.col_match = TableB.col_match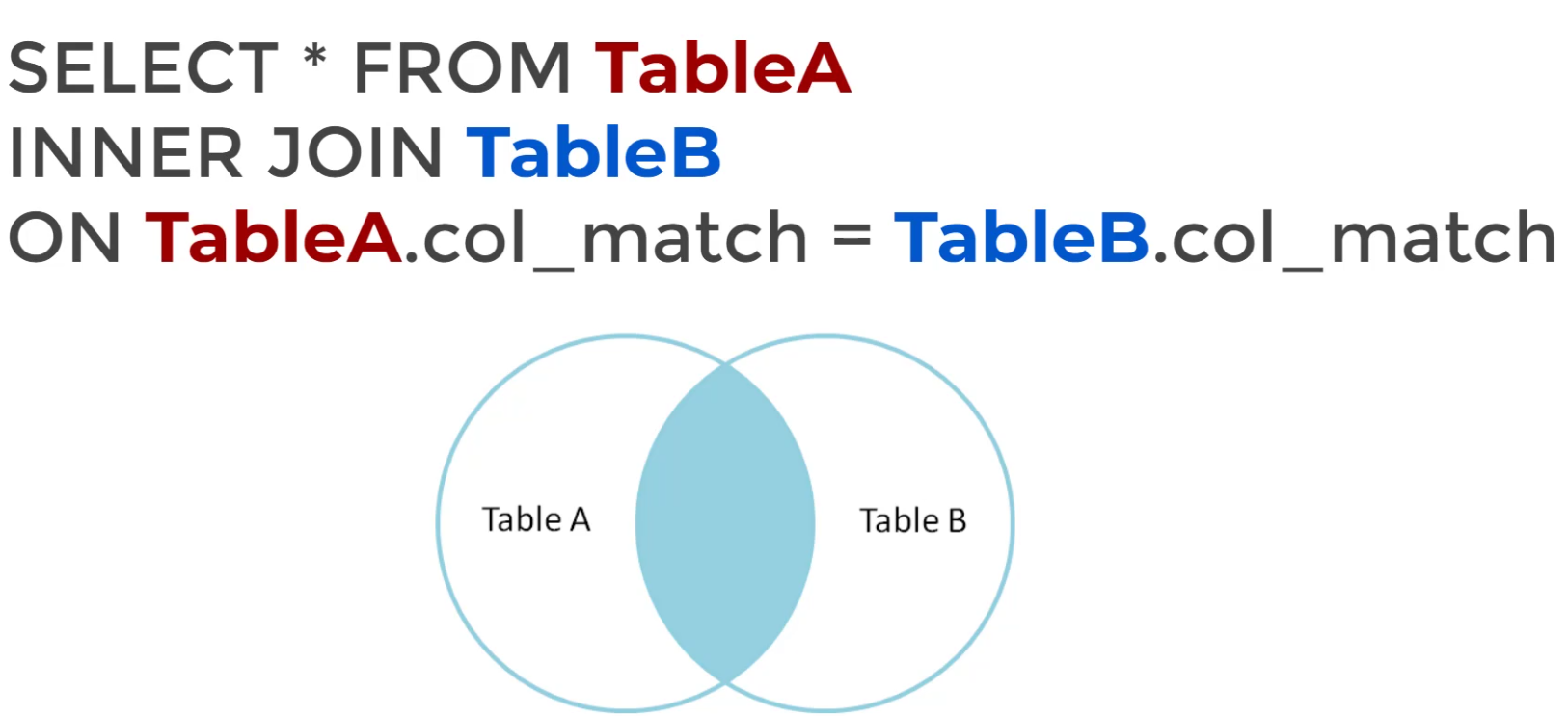
Note
Writing
joinon its own will usually be treated as an inner join in most SQL engines.
Example
Given two tables:
Customers
| id | name | city |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alice | New York |
| 2 | Bob | Chicago |
| 3 | Charlie | San Diego |
Orders
| id | customer_id | product |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Laptop |
| 2 | 1 | Keyboard |
| 3 | 3 | Monitor |
Using an INNER JOIN to retrieve customers who have placed orders:
SELECT Customers.name, Orders.product
FROM Customers
INNER JOIN Orders ON Customers.id = Orders.customer_id;Result:
| name | product |
|---|---|
| Alice | Laptop |
| Alice | Keyboard |
| Charlie | Monitor |
Key Differences from Other Joins:
- Unlike a LEFT JOIN, which includes unmatched rows from the left table, an INNER JOIN only includes matches.
- Unlike a RIGHT JOIN, which includes unmatched rows from the right table, an INNER JOIN only includes matches.
- Unlike a FULL OUTER JOIN, which includes unmatched rows from both tables, an INNER JOIN filters them out.