CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) was introduced in 1993 to fix a problem with IP Address Classes where if a company had more than 254 hosts (the limit for a Class C IP network), they would have to be assigned a Class B network. However, unless that company used most of the 65,534 hosts available, the global IP address space saw much wastage.
Under CIDR, the fixed /8, /16, and /24 requirements for address classes were removed, allowing the network addresses to be subnetted into smaller networks (such as 175.10.10.0/20, for example, rather than the original Class B 175.0.0.0/16 range).
Route summarisation
Another benefit of CIDR is that aggregate blocks of networks can be advertised together on the internet. For example:
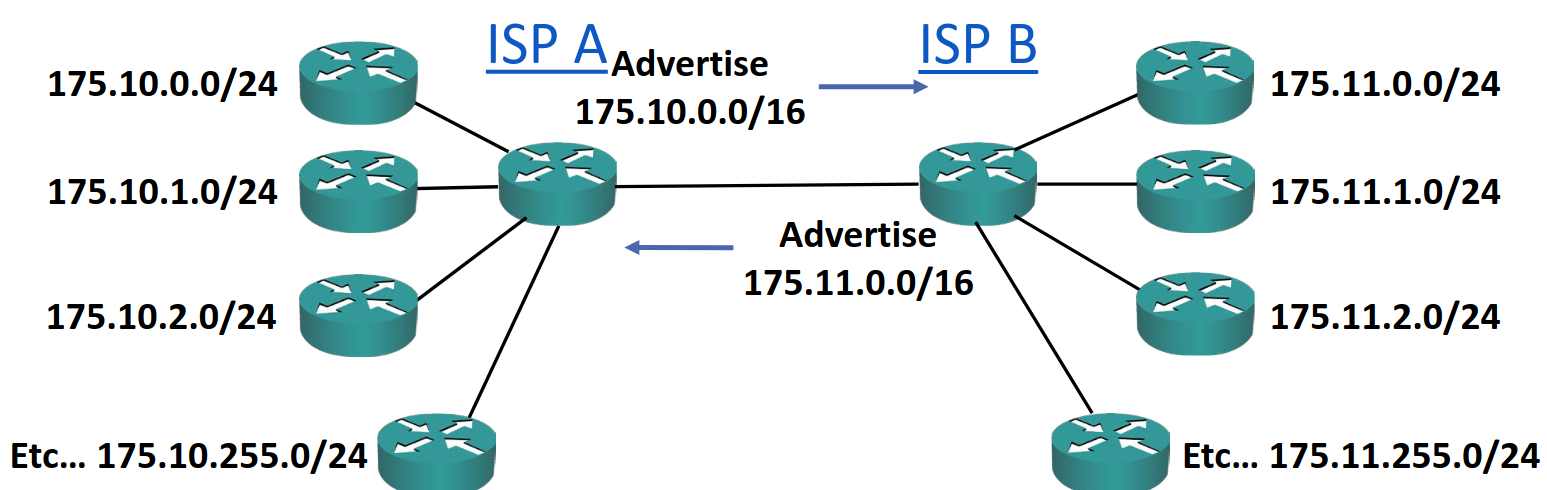
Note how the advertised routes are a /16 but the individual blocks assigned are all /24. This means each ISP does not have to advertise each and every single IP assignment to other ISPs, etc.